Utilizing Off-network Host to Connect with On-network Host
The title may be a bit confusing, but those familiar with internal network penetration must have encountered such a scenario. Let's get straight to the point.
Here, we assume that Host A (192.168.146.1) is the on-network host and Host B (192.168.146.12) is the off-network host.
The On-network Host Can Access a Certain Port of the Off-network Host
This scenario generally uses
Internal Network Routingandbind_tcptype listening to achieve the connection ofHost B.
Host Ais connected normally.

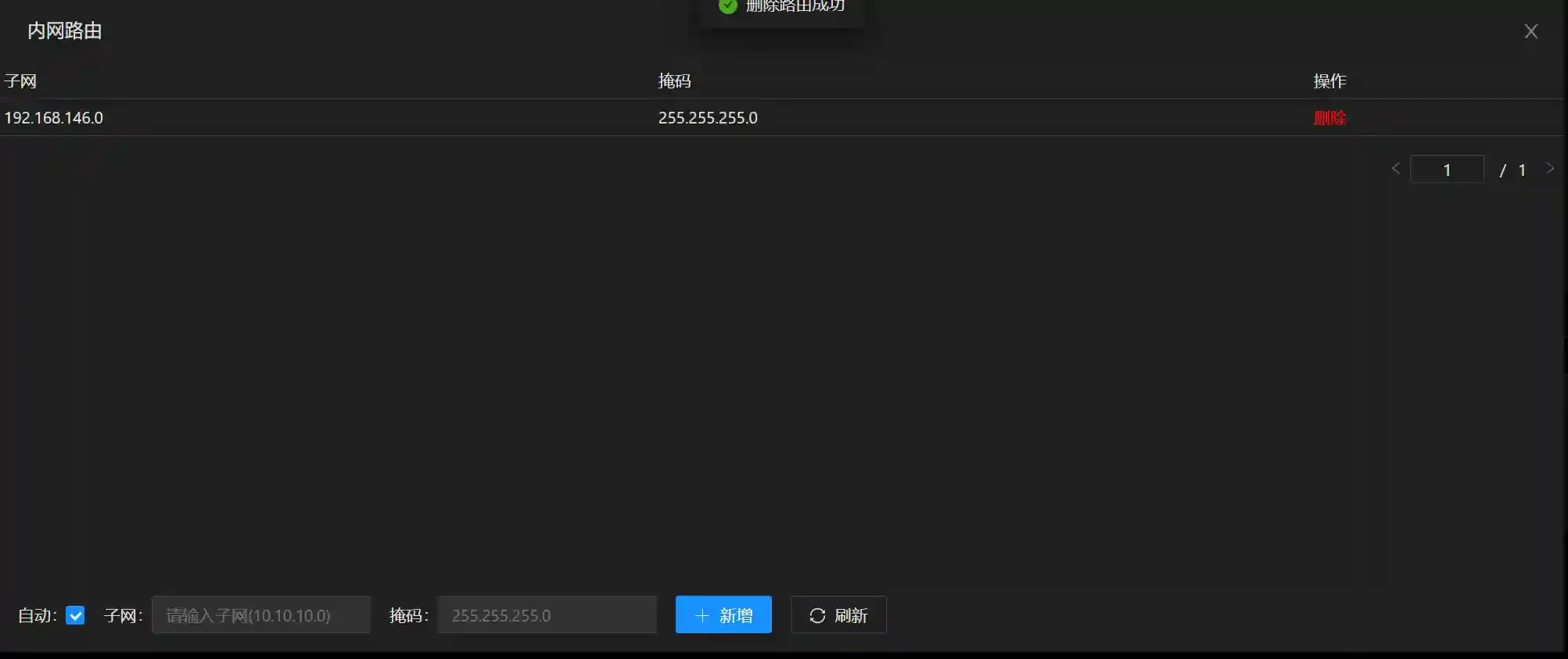
Add a route to the 192.168.146.0/24 network segment.
Generate a bind_tcp payload and execute it on
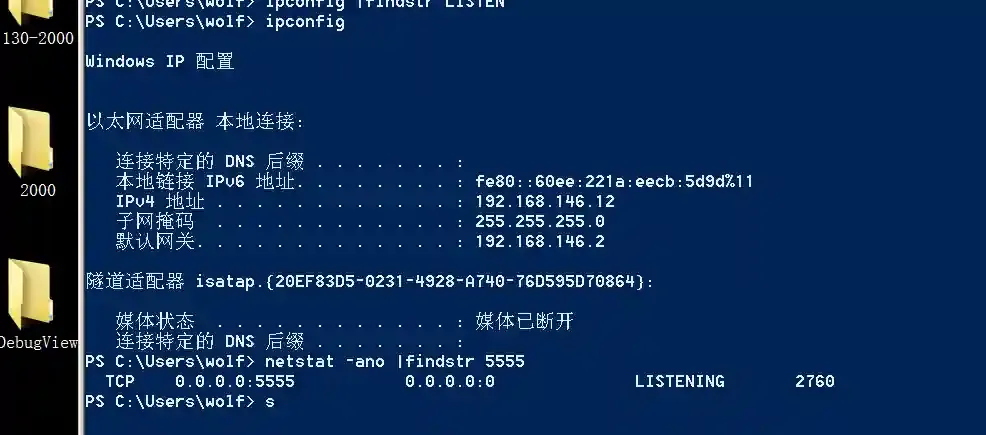
Host B(in actual combat, it is executed through exp).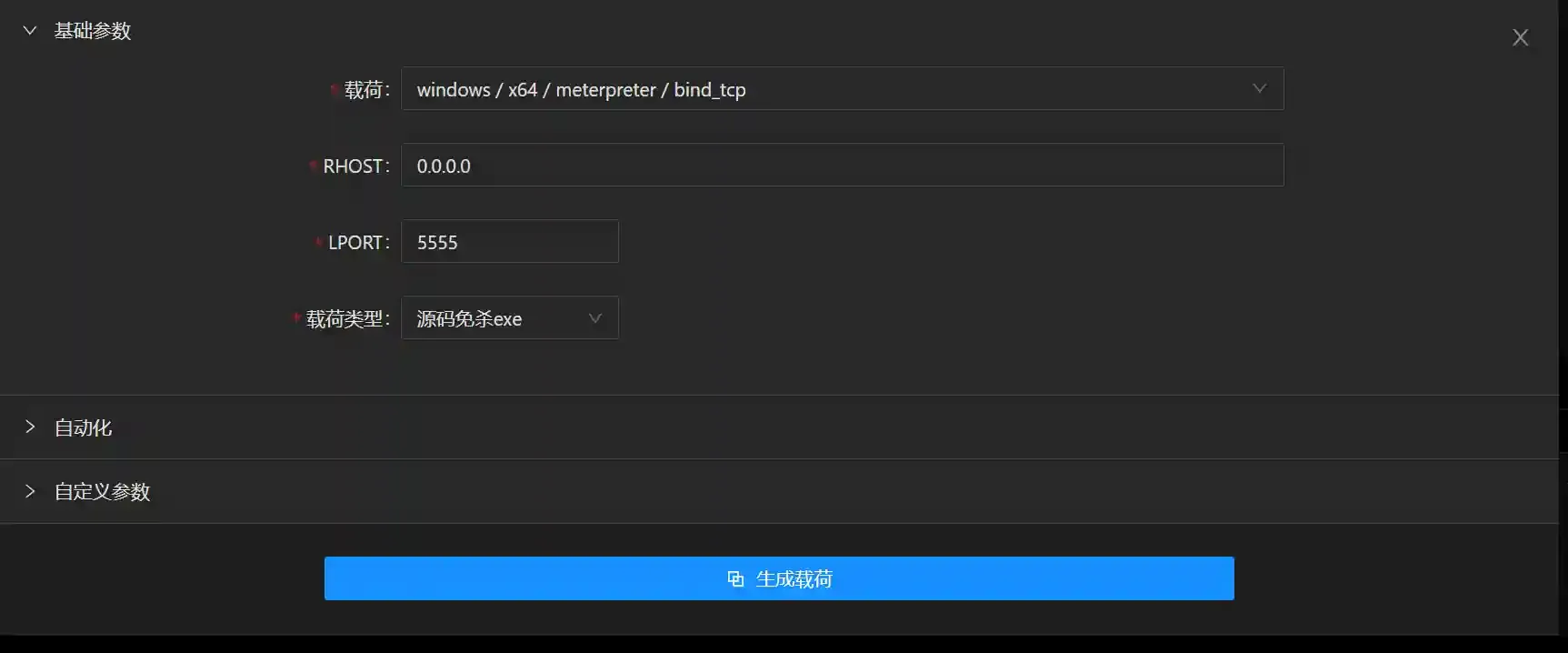
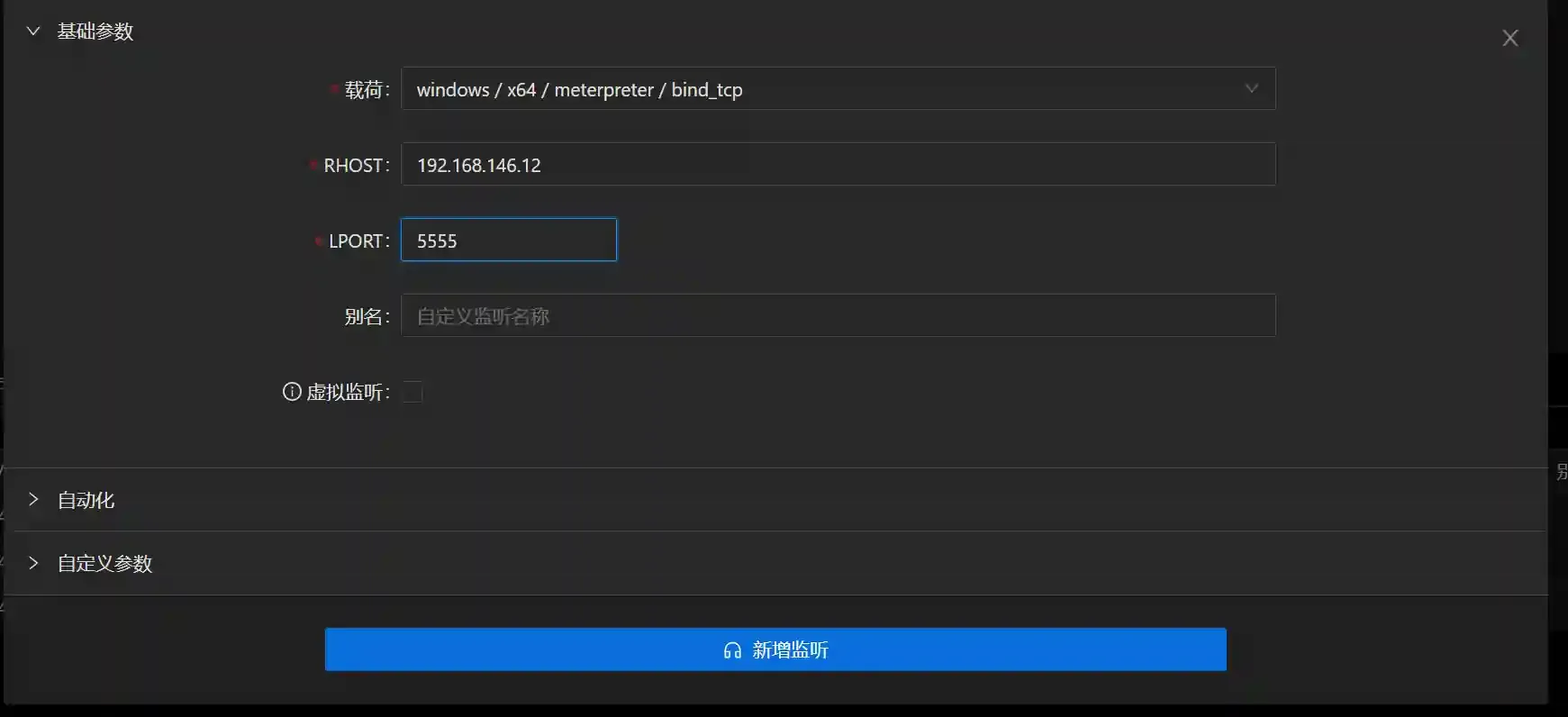
Run a listening pointing to
Host B.
Host Bis connected.
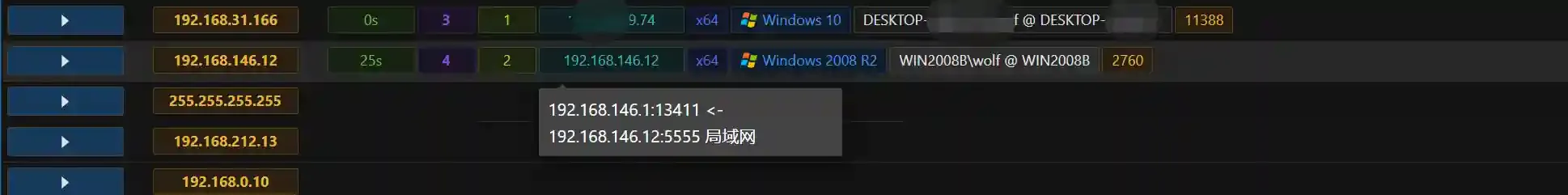
It can be seen that the Session connection information of Host B is through Host A (192.168.146.1).
The Off-network Host Can Access a Certain Port of the On-network Host
This scenario uses
Reverse Port Forwardingandreverse_tcptype listening payload to achieve.
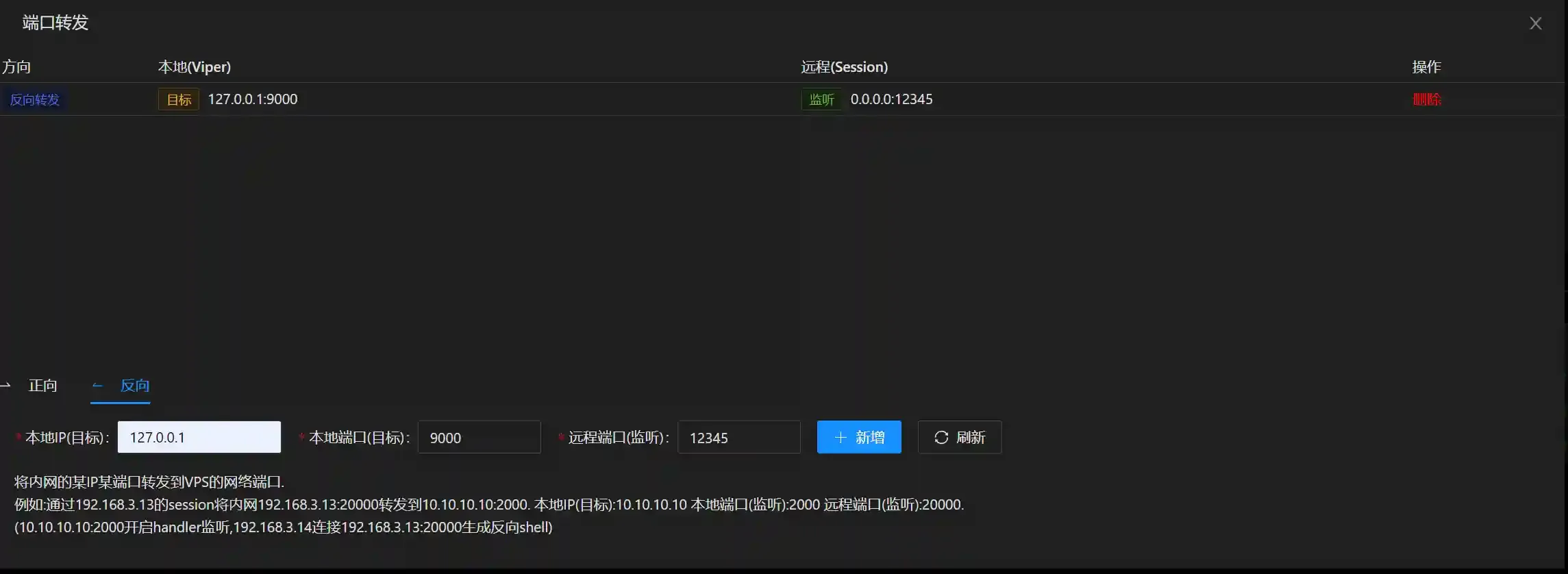
Host Ais connected normally.Add a reverse_tcp_rc4 type listening and remember to use the 9000 port here.
Do not use the reverse_https type.

- Add a reverse port forwarding and remember to use the 9000 port and 12345 port here.
This operation requires administrator privileges that have passed UAC.
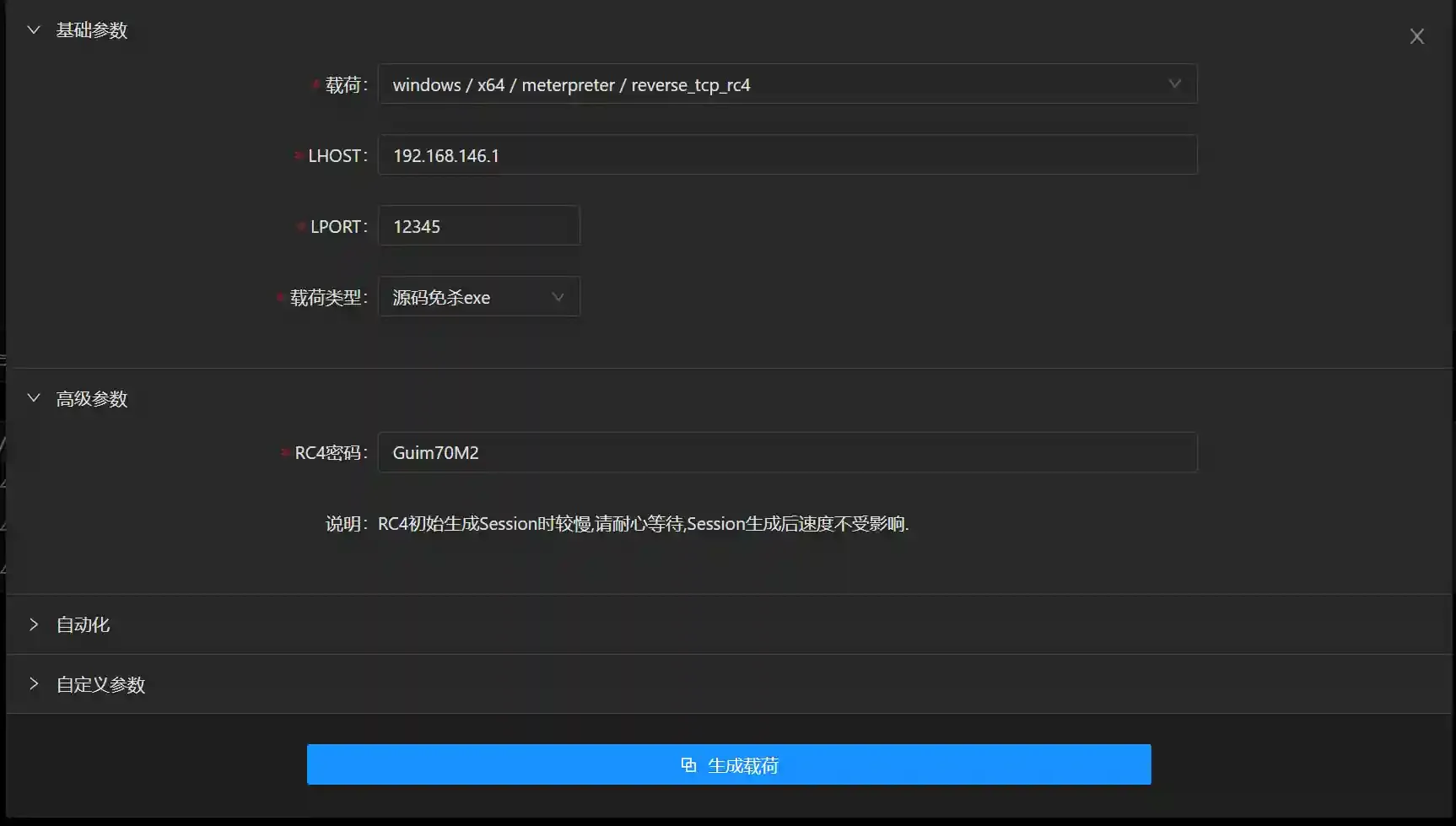
- Generate a reverse_tcp_rc4 type payload and execute it on
Host B.
Please pay attention to the following parameters here.
Fill in the internal network IP address (192.168.146.1) of the on-network host in LHOST.
Fill in the address (12345) of the remote port (listening) in the previous port forwarding in LPORT.
The RC4 password must be the same as the RC4 password established when listening before.
Host Bis connected.

Because reverse port forwarding is used, the Session connection information is the 127.0.0.1 loopback address.